Kubernetes in Docker - local clusters for testing Kubernetes
$ go install sigs.k8s.io/[email protected] && time kind create cluster
kind - Kubernetes in Docker, is a tool for running local Kubernetes clusters using Docker container “nodes”. kind was primarily designed for testing Kubernetes itself, but may be used for local development or CI, as well as proof-of-concept before upgrade current running cluster in production.
Features
- Spin up, tear down and rebuild clusters in seconds—literally.
- Runs with limited compute resources : a single CPU core and 1 GB of RAM is already enough.
- supports multi-node (including HA) clusters; of course, more nodes need more resources.
- Pick whichever Kubernetes version you’d like to test.
- Built-in Load Balancer: Cloud Provider KIND, Ingress, and Gateway API.
- Supports Linux, macOS and Windows.
Pre-requisite
Installing Go
Installing Docker
Installing kubectl
Installing Helm CLI and
Installing Cilium CLI
Install KinD
Follow the instructions of KinD official GitHub Repo or Quick Start guide for platform specific.
$ brew install kind
$ [ $(uname -m) = x86_64 ] && curl -Lo ./kind https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/dl/v0.30.0/kind-$(uname)-amd64
$ chmod +x ./kind
$ sudo mv ./kind /usr/local/bin/kind
Create a single node cluster with specific Kubernetes version
$ kind create cluster --image kindest/node:v1.33.4
Advanced Usage
Use a configuration file for advanced scenarios: For more complex configurations, such as multi-node clusters or custom networking, you can define the image in a YAML configuration file.
Create a cluster with standard Kubernetes API server address and port
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
networking:
apiServerAddress: "0.0.0.0" # Binds to all interfaces
apiServerPort: 6443 # Default Kubernetes API port
Save file and issue command.
$ kind create cluster --config kind-config.yaml
Create multi-nodes cluster
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane
image: kindest/node:v1.34
- role: worker
image: kindest/node:v1.34
- role: worker
image: kindest/node:v1.34
- role: worker
image: kindest/node:v1.34
Now you're all set to create cluster :
$ kind create cluster --config kind-multi-nodes-config.yaml
Create a multi-node HA cluster with Cilium CNI
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane
- role: control-plane
- role: worker
- role: worker
- role: worker
networking:
disableDefaultCNI: true
kubeProxyMode: none
Then create an HA cluster without kube-proxy:
$ kind create cluster --config kind-no-proxy-config.yaml
L3/L7 Traffic Management
If you plan to enable Cilium Gateway API feature, the Gateway API CRDs must be installed first.
Recommended : Kubernetes Gateway API
Gateway API is ideal for large-scale cluster (i.e. 10+ workers and 100+ services). In addition to drop-in traditional Ingress Controller features, it also supports HTTP2/gRPC/WebSocket.
Install Gateway API CRDs:
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/releases/download/v1.3.0/standard-install.yaml
Ensure that installation was successfully.
$ kubectl get crd gatewayclasses.gateway.networking.k8s.io
Optional : Ingress Controller
$ kubectl apply -f https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/examples/ingress/deploy-ingress-nginx.yaml
$ kubectl wait --namespace ingress-nginx \
--for=condition=ready pod \
--selector=app.kubernetes.io/component=controller \
--timeout=90s
$ kubectl apply -f https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/examples/ingress/usage.yaml
$ kubectl -n ingress-nginx get services
Install Cilium CNI:
$ cilium install --set kubeProxyReplacement=true --set gatewayAPI.enabled=true && cilium status --wait
Verify installation successfully:
$ cilium config view
$ kubectl get nodes -o wide
L2 Load-balancer
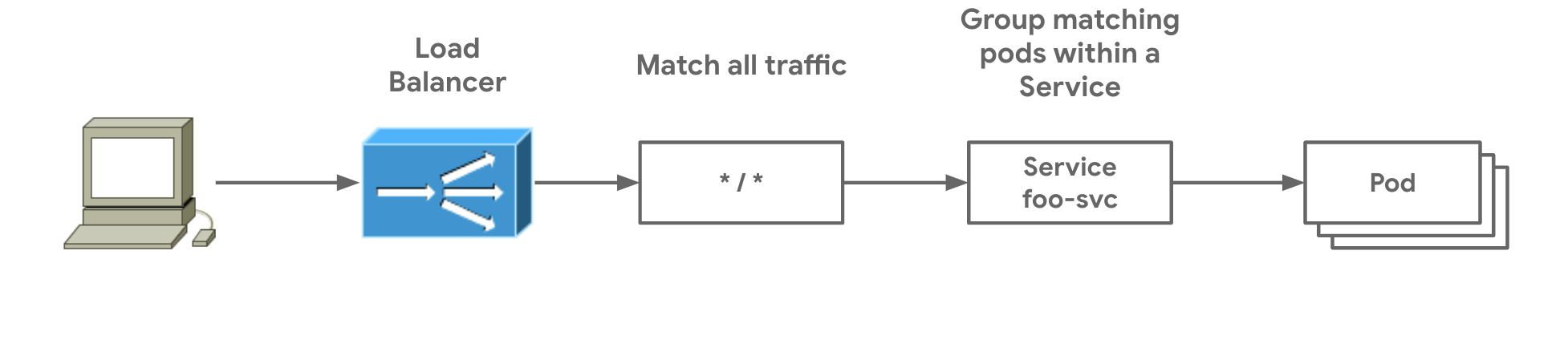
Option 1 : using Cloud Provider KIND
Cloud Provider KIND brings up the Kubernetes service of type LoadBalancer working in a KinD cluster.
To install it using Go:
$ go install sigs.k8s.io/cloud-provider-kind@latest
$ sudo install ~/go/bin/cloud-provider-kind /usr/local/bin
Run Cloud Provider KIND as a foreground process.
$ tmux new -s cloud-provider-kind
$ cloud-provider-kind
Option 2 : using MetalLB
Install MetalLB:
$ helm repo add metallb https://metallb.github.io/metallb
$ helm install metallb metallb/metallb --namespace metallb-system --create-namespace
Wait til all pod STATUS are READY then configure MetalLB.
$ kubectl wait --namespace metallb-system --for=condition=ready pod --selector=app.kubernetes.io/name=metallb --timeout=240s
Configure MetalLB:
Get Docker network that KinD is running on:
$ docker network inspect kind | jq .[].IPAM.Config
Output
[
{
"Subnet": "172.18.0.0/16",
"Gateway": "172.18.0.1"
},
{
"Subnet": "fc00:f853:ccd:e793::/64",
"Gateway": "fc00:f853:ccd:e793::1"
}
]
Create an IPAddressPool Resource.
---
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: IPAddressPool
metadata:
name: kind-pool
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
addresses:
- 172.18.255.1-172.18.255.254 # Use the last IPv4 subnet CIDR from the docker command.
autoAssign: true
avoidBuggyIPs: false
---
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: L2Advertisement
metadata:
name: lb
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
ipAddressPools:
- kind-pool
$ kubectl apply -f metallb-config.yaml
To verify:
$ kubectl create deployment kubernetes-bootcamp --image=gcr.io/google-samples/kubernetes-bootcamp:v1
$ kubectl expose deployment/kubernetes-bootcamp --type="LoadBalancer" --port 8080
$ EXTERNAL_IP=$(kubectl get svc kubernetes-bootcamp -o json | jq -r '.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip')
$ curl http://$EXTERNAL_IP:8080/
Hello Kubernetes bootcamp! | Running on: kubernetes-bootcamp-658f6cbd58-mnrnx | v=1
Real-world Scenario
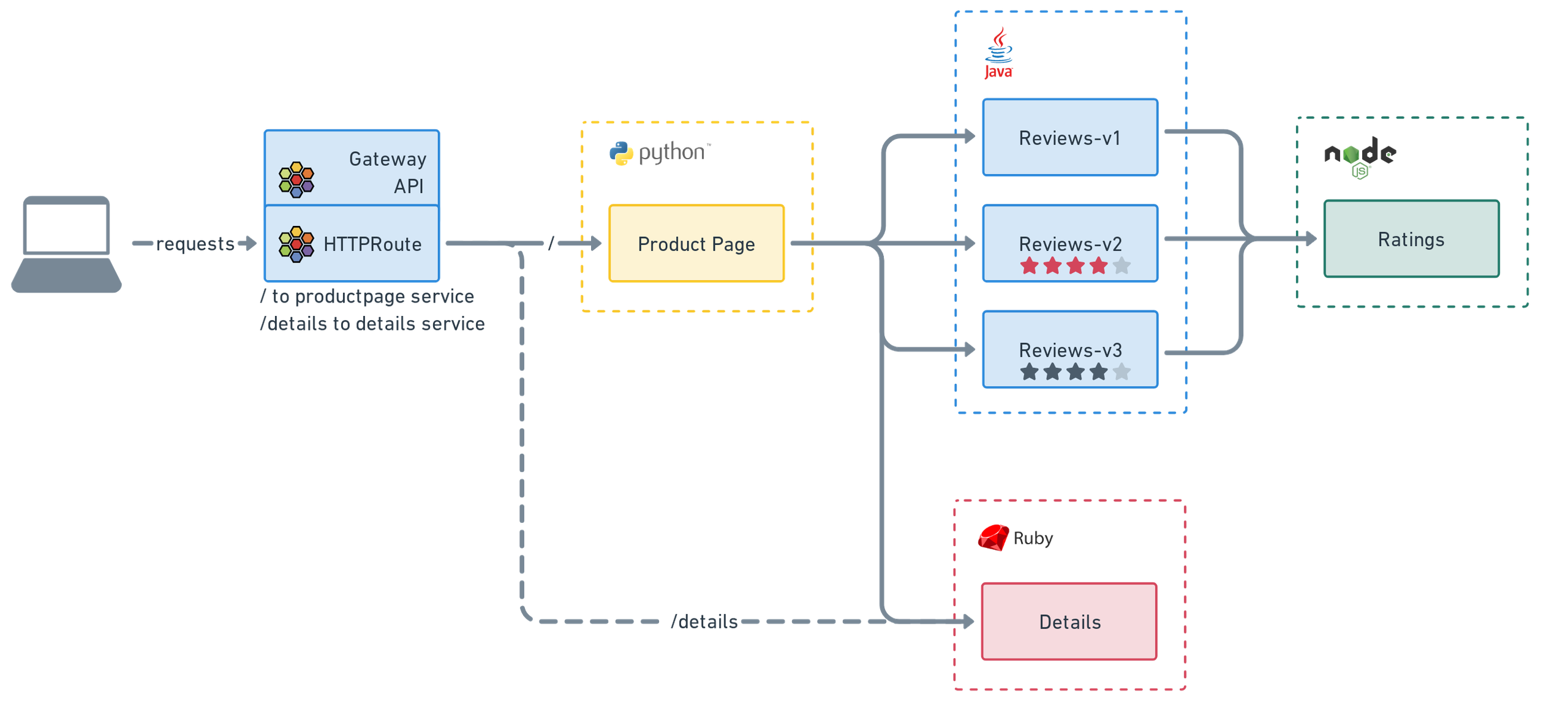
Deploying Bookinfo Demo Applications
Verify success by installing Istio's Bookinfo applications and Cilium's Gateway with HTTPRoutes:
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.27/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.18.0/examples/kubernetes/gateway/basic-http.yaml
$ kubectl get svc cilium-gateway-my-gateway
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
cilium-gateway-my-gateway LoadBalancer 10.96.190.51 172.18.255.1 80:32243/TCP 30s
$ kubectl get gateway
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
my-gateway cilium 172.18.255.1 True 98s
$ GATEWAY=$(kubectl get gateway my-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
$ curl -v -H 'magic: foo' http://"$GATEWAY"\?great\=example
$ curl --fail -s http://$GATEWAY/details/1 | jq .
Output
{
"id": 1,
"author": "William Shakespeare",
"year": 1595,
"type": "paperback",
"pages": 200,
"publisher": "PublisherA",
"language": "English",
"ISBN-10": "1234567890",
"ISBN-13": "123-1234567890"
}
HTTPS with self-signed TLS certificate
Create a certificate:
$ mkcert '*.cilium.rocks'
Output
Created a new local CA 💥
Note: the local CA is not installed in the system trust store.
Run "mkcert -install" for certificates to be trusted automatically ⚠️
Created a new certificate valid for the following names 📜
- "*.cilium.rocks"
Reminder: X.509 wildcards only go one level deep, so this won't match a.b.cilium.rocks ℹ️
The certificate is at "./_wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem" and the key at "./_wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem" ✅
It will expire on 18 December 2027 🗓
Let's now create a Kubernetes TLS secret with this key and certificate:
$ kubectl create secret tls ca --key=_wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem --cert=_wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem
Deploy Gateway for HTTPS traffic
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.18.2/examples/kubernetes/gateway/basic-https.yaml
Edit the /etc/hosts file
$ GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl get gateway tls-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
$ cat << EOF >> /etc/hosts
${GATEWAY_IP} bookinfo.cilium.rocks
${GATEWAY_IP} hipstershop.cilium.rocks
EOF
Install self-signed certificates
$ mkcert -install
Ensure that HTTPS works
$ curl -s https://bookinfo.cilium.rocks/details/1 | jq .
Chances are you running KinD on a remote host and need to send traffic to KinD node IPs from a different host than where KinD is running.
On remote KinD host:
Get load-balancer IP of the service exposing by KinD node.
$ LB_IP=$(kubectl get svc cilium-gateway-my-gateway -o json | jq -r '.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip')
*Replace cilium-gateway-my-gateway with your intended service. Run $ kubectl get svc if not sure.
$ echo $LB_IP
On local SSH client:
$ ssh -L 8080:<$LB_IP>:80 username@<SSH-SERVER>
Delete KinD Cluster
$ kind delete cluster